Istanbul, Turkey, 10 September 2016
In Istanbul, extraordinary experiences are found around every corner.

Here, dervishes whirl, müezzins call from minarets and people move between continents multiple times a day.

Istanbul is home to millenia-old monuments and cutting edge art galleries – sometimes on the same block.
It is an utterly beguiling city full of sumptous palaces, domes and minarets, cobblestone streets and old wooden houses, squalid concrete apartment blocks and graceful Art Nouveau apartments, international fashion shops cheek and jowl next to bazaars and beggars, street vendors and stray dogs and wild cats, the beauty of the Bosphorus and the promising spell of the Orient.
Vast labyrinths of narrow covered passageways and wide boulevards lined with superb fin-de-siecle architecture, the breathtaking interior of the Blue Mosque, the smells and sounds of the markets, tiny boats vying with huge tankers for a piece of the waterfront, street hustlers and people bum-to-bum striving to navigate alleyway and passage…

This is the Istanbul I fell in love with, the Istanbul that remains with me as poignant as one´s memories of former intimates.

Istanbul attracts millions of tourists every year but as well it draws into itself many who have come in search of work, of a new life, for a chance to thrive here where fortune is denied elsewhere.
It is my last day in Istanbul and my heart feels as sad as the inevitable farewell that must be said to a loved one leaving whose return is uncertain.
I am in the Sultanahmet district where tourists congregate and the locals bend over backwards to accommodate to their every whim no matter how unreasonable these whims might be.
This is a neighbourhood where one stands beneath magnificent domes or inside opulent palaces, where history is experienced by all one´s senses, where one can explore the watery damp depths of the Basilica Cistern then surrender to the steam of a hamam.

Wander through the produce markets, then join the locals in smoking nargiles, drinking tea and playing backgammon.

I stand outside the Metropolis Hostel, on a quiet side street awaiting my shuttle bus to the airport and talk quietly to one of the co-owners of this very friendly, very comfortable, very clean, home away from home.

He is a Kurd and he talks about his life in Istanbul and what transpired to lead him to this city so very distant from his home in Batman in faraway southeastern Turkey.
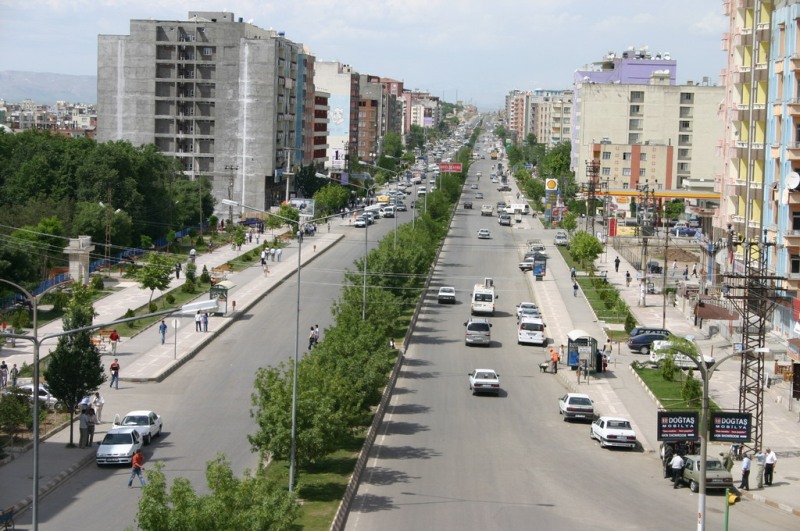

Above: City centre, Batman, Turkey
I have no political feelings towards either the Kurds or the Turks, except sadness that neither side sees a possibility of peace and cooperation with one another.
He speaks of battlefields where Kurd has fought ISIS warrior and Turk has bombed Kurd despite their common enemy.

He speaks of devastation and death, of friends and family forever affected by loss and injury.
There are no words of comfort I can give him, for I am an ignorant foreigner, on a mini-visit to Istanbul before attending a friend´s wedding in Antalya the very next day.
He speaks of how the Syrian civil war has driven many Syrians into Turkey competing for the same jobs as those already resident here.

Above: Map of the Syrian Civil War
He tells me of how bombings and attacks of ISIS upon Turkey and Kurd upon Turk and Turk upon Kurd have drastically reduced tourism in Istanbul to a third of what it once was.
I leave Istanbul and this Kurd with much of his pain unspoken and distract myself with the Antalya events that await me.
But it is nonetheless an uneasy departure filled with helplessness and sadness.
Landschlacht, Switzerland, 23 January 2017
I often wish I were a wiser man, more knowledgeable in the ways of politics and psychology.
I find myself uncertain of whether I should hate those who have caused indescribable sorrow, for the Turks I have met both within and outside Turkey have always been friendly towards me, as have the few Kurds I have met as well.
I am rational enough to know that those who murder in the name of Allah are not true followers of Muhammed or Islam, so the gullible who have followed the infidels of ISIS have done so either out of ignorance or hope that those governments that failed them will be supplanted by a new order, albeit a dark order, that offers some sort of security through fear and intimidation.

I refuse to hate all the individuals caught up in forces unleashed by those that wield power without compassion, but instead find fault with those who claim to serve their fellow man yet use their fellow man for power, gain and profit.
Now, it is a fair question for any reader to ask:
Why should I care?
And why the history lessons?
We are all human beings, a few saints and monsters amongst us, but most of us are decent basic human beings in the pursuit of happiness.
I think we tend to forget this.
We are all so focused on what makes us different and in our fear use these differences to do unspeakable acts towards one another.
But I firmly believe that there is more that connects us than divides us.
We are bound by love and compassion, by conscience and will, by strength and weakness, by morality and mortality.
In looking at the complexities and tragedies of the ongoing saga of Turkey, or any other part of the world for that matter, I hope to understand the mindsets of both sides of this conflict and hope, in my own humble and naive fashion, to offer a possible idea that might help.
We are all interconnected and what happens in faraway places eventually find its way – by sometimes subtle, sometimes powerful means – to our own doorsteps.
I explore history, because by trying to understand what leads people to where they are now, why they think and act the way they do, helps to comprehend who they are and, perhaps, as well, avoid some of the mistakes people make in this ongoing, neverending process of life and time.
In part 1 of this blog post I wrote of events in Kurdish / Turkish history – from ancient times until the Sixties – including the 9 January bombing in Izmir – that compelled me to discuss the problems that plague a country I love.

Prior to the Sixties, the record shows again and again brutal violence towards and suppression of the Kurdish people by the Turks, responded to by armed Kurdish rebellion when it appeared that all attempts at negotiation were impossible:
“Thousands of Kurds, including women and children, were slain.
Others, mostly children, were thrown into the Euphrates, while thousands of others in less hostile areas, who had first been deprived of their cattle and other belongings, were deported to provinces in central Anatolia.
It is now stated that the Kurdish question no longer exists in Turkey.” (British Council, 1938)
In Part One, we examined the Kurdish perspective.
But what has led the Turkish people, especially its governments, to respond to the Kurds in the manner in which they have?
Why has President Recep Erdogan reacted to events both domestic and international in the manner that he has?

To understand His Excellency, to understand the Turkish point-of-view, (not always the same) we need to travel back in time once more:
27 May 1960:
A coup d’ état is staged by a group of 38 young Turkish military officers.
It is a time of socio-political turmoil and economic hardship as US aid from the Truman Doctrine and the Marshall Plan is running out.
Prime Minister Adnan Menderes plans a visit to Moscow in the hope of establishing alternative lines of credit.
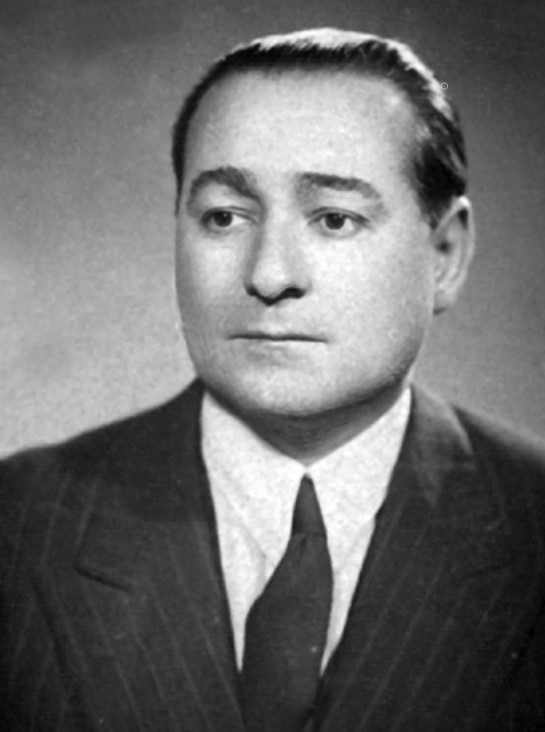

Above: Adnan Menderes (1899 – 1961), 9th Prime Minister of Turkey (1950 – 1960)
Colonel Alparslan Türkes orchestrates the plot and declares the coup over radio to announce “the end of one period in Turkish history and usher in a new one.”

Above: Alparslan Turkes (1917 – 1997)
The Great Turkish Nation:
Starting at 3 am on 27 May, the Turkish armed forces have taken over administration throughout the entire country.
This operation, thanks to the close cooperation of all our citizens and security forces, has succeeded without loss of life.
Until further notice, a curfew has been imposed, exmept only to members of the armed forces.
We request our citizens to facilitate the duty of our armed forces and assist in reestablishing the nationally desired democratic regime.”
In a press conference held on the following day, General Cemal Gürsel emphasizes that the “purpose and the aim of the coup is to bring the country with all speed to a fair, clean and solid democracy.”

Above: Cemal Gursel (1895 – 1966), 4th President of Turkey (1960 – 1966)
I want to transfer power and the administration of the nation to the free choice of the people.”
The coup removes a democratically elected government while expressing the intent to install a democratically elected government.
235 generals and more than 3,000 commissioned officers are forced to retire.
More than 500 judges and 1,400 university faculty members lose their jobs.
The chief of the General Staff, the President, the Prime Minister and other members of the administration are arrested.
General Gürsel is appointed provisional head of state, Prime Minister and the Minister of Defense.
Minister of the Interior Namik Gedik commits suicide while he is detained in the Turkish Military Academy.
President Celal Bayar, Prime Minister Adnan Menderes and several other members of the administration are put on trial before a court appointed by the ruling junta on the island of Yassuda in the Sea of Marmara.
The politicians are charged with high treason, misuse of public funds and abrogation of the Turkish constitution.
16 September 1961:
Prime Minister Adnan Menderes, Minister of Foreign Affairs Fatin Rüstü Zorlu and Finance Minister Hasan Polatkan are executed on Imrali Island.
(Imrali Island Prison is known as the place where American Billy Hayes was incarcerated later telling his story in Midnight Express and where PKK leader Abdullah Ocalan has been imprisoned since 1999.)

Above: Poster of the film adaptation (1978)
A month later, administrative authority is returned to civilians.
In the first free election after the coup, Süleyman Demirel is elected in 1965.

Above: Suleyman Demirel (1924 – 2015), 9th President of Turkey (1993 – 2000)
As the 1960s wear on, violence and instability plague Turkey.
Economic recession sparks a wave of social unrest marked by student demonstrations, labour strikes and political assassinations.
On the left, worker and student movements are formed.
On the right, Islamist and militant nationalist groups counter them.
The Revolutionary Youth Federation of Turkey (DEV-GENC) is founded in 1965 and it will inspire various other organisations, including Devrimci Yol, the Revolutionary Workers and Peasants Party of Turkey and the Kurdistan Workers´ Party.
DEV-GENC members set US Ambassador Robert Komer´s car on fire in 1969 while he is visiting an Ankara campus, participate in the protests against the US 6th Fleet anchoring in Turkey from June 1967 to February 1969, and also play an active role in the workers´ actions on 15 – 16 June 1970.

Above: Robert Komer (1922 – 2000) (left) in meeting with US President Lyndon Johnson
CIA agent Aldrich Ames is able to unveil the identity of a large number of members.

Above: Aldrich Ames (b. 1941), CIA – KGB double agent, presently incarcerated in Allenwood Penitentiary
The Grey Wolves, a Turkish nationalist paramilitary youth organisation, often described by its critics as an ultra-nationalist or neo-fascist death squad, are responsible for matching and surpassing the left´s violent activities, engaging in urban guerilla warfare with left-wing activists and militants.

On the political front, Prime Minister Demirel´s center-right Justice Party government is experiencing trouble.
Various factions within the Party defect to form groups of their own, gradually reducing the Party´s parliamentary majority and bringing the legislative process to a halt.
By January 1971, Turkey is in a state of chaos.
Universities have ceased to function.
Students rob banks and kidnap US servicemen and attack American targets.
University professors critical of the government have their homes bombed by neo-fascist militants.
Factories are on strike and many workdays are lost.
The Islamist movement becomes more aggressive and openly rejects Atatürk and Kemalism, thus infuriating the armed forces.
The government, weakened by defections, seems paralysed, powerless to curb campus and street violence and unable to pass any serious legislation on social and financial reform.
12 March 1971:
The Chief of the General Staff Memduh Tagmac hands the Prime Minister a Memorandum – an ultimatum by the armed forces – demanding “the formation, within the context of democratic principles, of a strong and credible government, which will neutralise the current anarchical situation and which, inspired by Atatürk´s views, will implement the reformist laws envisaged by the constitution”, putting an end to the “anarchy, fratricidal strife, and social and economic unrest.”
If the demands are not met, the army would “exercise its constitutional duty” and take over power itself.
Demeril resigns after a three-hour meeting with his cabinet.
The coup doesn´t surprise most Turks, but what direction will the coup take the country?
Who is in charge?
The “restoration of law and order” is given priority.
The left is to be suppressed in an attempt to curb trade union militancy and the demands for higher wages and better working conditions.
The public prosecutor opens a case against the Workers’ Party of Turkey for carrying out Communist propaganda and supporting Kurdish separatism.
All youth organisations affliated with DEV-GENC are to be closed, as they are blamed for the left-wing youth violence and university and urban unrest plaguing the country.
Police searches in offices of teachers’ unions and university clubs are carried out.
Such actions encourage the right who target provincial teachers and Workers’ Party supporters.
The commanders who have seized power are reluctant to exercise it directly, so the regime rests on an unstable balance of power between civilian politicians and the military.
It is neither a normal elected government nor an outright military dictatorship which can entirely ignore parliamentary opposition.
In April, a new wave of terror begins, carried out by the Turkish People’s Liberation Army, in the form of kidnappings and bank robberies.
27 April 1971:
Martial law is declared in 11 of Turkey´s 67 provinces, especially in major urban areas and Kurdish regions.
Youth organisations are banned, union meetings are prohibited, leftists publications are forbidden, and strikes are declared illegal.
After the Israeli consul is abducted on 17 May, hundreds of students, young academics, writers, trade unionists and Workers’ Party activists as well as people with liberal-progressive sympathies are detained and tortured.
The consul is shot four days later.
For the next two years, repression continues, with martial law renewed every two months.
Constitutional reforms repeal the essential liberal fragments of the constitution.
The National Intelligence Organisation (MIT) uses the Ziverbey Villa as a torture centre, employing physical and psychological coercion.
Interrogations, directed by CIA-trained specialists, result in hundreds of deaths or permanent injuries.
Among their victims is journalist Ugur Mumcu, arrested shortly after the coup, later writes that his torturers informed him that not even the President could touch them.

Above: Journalist Ugur Mumcu (1942 – 1993), assassinated 24 January 1993 in a car bomb outside his Ankara home (Cumhuriyet, 24 January 2003)
By the summer of 1973, the military-backed regime has achieved most of its political aims.
The constitution has been amended so as to strengthen the state against civil society.
Special courts are in place to deal with all forms of dissent quickly and ruthlessly.
Universities, their autonomy ended, have been made to curb the radicalism of students and faculty.
Radio, TV and newspapers are curtailed.
The National Security Council is much more powerful.
In October 1973 Bülent Ecevit wins the election and the problems that plagued the pre-coup government return.

Above: Mustafa Bulent Ecevit (1925 – 2006), 16th Prime Minister of Turkey (1974, 1977, 1978 – 1979, 1999 – 2002)
As the 1970s progress, the economy deteriorates, violence by the Grey Wolves escalates and intensifies, and left-wing groups as well commit acts aimed at causing chaos and demoralisation.
In 1975 Suleyman Demeril succeeds Ecevit as Prime Minister.
Demeril´s Justice Party forms a coalition with the Nationalist Front, the Islamist National Salvation Party and the Nationalist Movement Party.
There is no clear winner in the elections of 1977.
Demeril continues the coalition.
Ecevit returns to power in 1978, but Demeril regains it the following year.
By the end of the Seventies, Turkey is in turmoil, with unsolved economic and social problems, facing strike actions and political paralysis.
Since 1969, the proportional representational system has made it difficult to find any parliamentary majority.
Politicians are unable to combat the growing violence in the country.
The overall death toll of the Seventies is estimated at 5,000, with nearly ten assassinations per day.
16 March 1977, Istanbul
The University of Istanbul is attacked with a bomb and gunfire.
7 die, 41 injured.
1 May 1977, Istanbul
Labour Day has been celebrated in Istanbul since 1912.
500,000 people gather on Taksim Square.

Shots are heard coming from the building of the water supply company Sular Idaresi and the Marmara Hotel (in 1977, the tallest building in Istanbul).

Security forces intervene with armoured vehicles making much noise with their sirens and explosives.
They hose the crowd with pressurized water.
Many casualities are caused by the panic that this intervention creates.
42 people killed, 220 injured, most crushed.
None of the perpetrators are caught or brought to justice.
The CIA is suspected of involvement.
9 October 1978, Ankara
7 university students, members of the Turkish Workers’ Party, are assassinated by ultra-nationalists.

27 November 1978, Diyarbakir
The left-wing organisation is mostly made up of students led by Abdullah Ocalan in Ankara and focused on helping the large oppressed Kurdish population in southeast Turkey.
The violence of the times, especially the attacks on the University of Istanbul, the Taksim Square massacre and the assassinations in Ankara, compel the group, meeting here inside a teahouse, to adopt the name Kurdistan Workers’ Party (PKK) and a Marxist ideology to counter violence with violence.

19 – 26 December 1978, Kahramanmaras
Kahramanmaras is a city in the Mediterranean region of southern Turkey close to the Syrian border.
Above: The minaret of the Grand Mosque of Kahramanmaras
Kahramanmaras lies on a plain at the foot of Ahir Mountain and is best known for its production of salep (a flour made from dried orchids) and its distinctive ice cream.
It all starts with a noise bomb thrown into a cinema popular with right-wingers.
Rumours spread that left-wingers had thrown the bomb.
So, the next day a bomb is thrown into a coffee shop frequently visited by left-wingers.
The following evening known left-winger teachers Haci Colak and Mustafa Yuzbasioglu are killed on their way home.
While a crowd of over 5,000 people prepares for Colak’s and Yuzbasioglu’s funeral, right-wing groups stir up emotions saying that the Communists are going to bomb the mosque and massacre many Muslims.
On 23 December, things turn ugly.
Crowds storm the quarters where left-wingers live, destroying houses and shops.
The offices of the Confederation of Progressive Trade Unions of Turkey, the Teachers’ Association of Turkey, the Association of Police Officers and the Republican People’s Party are destroyed.
Over 100 people are killed and more than 200 houses and 100 shops destroyed.
“They started in the morning, burning all the houses, and continued into the afternoon.
A child was burned in a boiler.
They sacked everything.
We were in the water in the cellar, above us were wooden boards.
The boards were burning and falling on top of us.
My house was reduced to ashes.
We were with 8 people in the cellar.
They did not see us and left.” (Meryem Polat, one of the victims)
Martial law was declared across Turkey the following day.
Court cases, opened at military courts, lasted until 1991.
A total of 804 defendants, mostly right-wingers, were put on trial.
The courts passed 29 death penalties and sentenced 328 people to prison.
11 September 1979
General Kenan Evren orders a hand-written report on whether a coup is in order or the government merely needs a stern warning.

Above: Kenan Evren (1917 – 2015), 7th President of Turkey (1980 – 1989)
21 December 1979
The War Academy generals convene to decide a course of action.
The pretext for a coup is to put to an end the social conflicts plaguing the country as well as the political instability.
12 September 1980
The Turkish economy is on the verge of collapse with triple digit inflation, large scale unemployment and a chronic foreign trade deficit.
The National Security Council, headed by Evren, declares a coup d’etat, extending martial law throughout the country, abolishing the government and Parliament, suspending the Constitution and banning all political parties and trade unions.
The Council invokes the Kemalist tradition of state secularism and in national unity, presenting themselves as opposed to communism, facism, separatism and religious sectarianism.
The Council aims to unite Turkey with the global economy and give companies the ability to market products and services worldwide.
“A feeling of hope is evident among international bankers that Turkey’s military coup may have opened the way to greater political stability as an essential prerequisite for the revitalisation of the Turkish economy.” (International Banking Review, October 1980)
During 1980 – 1983, the foreign exchange rate was allowed to float freely, foreign investment encouraged, land reform projects promoted, export vigourously driven and wages frozen.
The Council rounded up members of both the right and left for trial by military tribunals.
- 650,000 people were under arrest.
- 1,683,000 people were blacklisted.
- 230,000 people were tried in 210,000 lawsuits.
- 7,000 people were recommended for the death penalty.
- 517 persons were sentenced to death.
- 50 of those given the death penalty were executed (26 political prisoners, 23 criminal offenders and 1 ASALA militant).
- The files of 259 people, which had been recommended for the death penalty, were sent to the National Assembly.
- 71,000 people were tried by articles 141, 142 and 163 of Turkish Penal Code.
- 98,404 people were tried on charges of being members of a leftist, a rightist, a nationalist, a conservative, etc. organization.
- 388,000 people were denied a passport.
- 30,000 people were dismissed from their firms because they were suspects.
- 14,000 people had their citizenship revoked.
- 30,000 people went abroad as political refugees.
- 300 people died in a suspicious manner.
- 171 people died by reason of torture.
- 937 films were banned because they were found objectionable.
- 23,677 associations had their activities stopped.
- 3,854 teachers, 120 lecturers and 47 judges were dismissed.
- 400 journalists were recommended a total of 4,000 years imprisonment.
- Journalists were sentenced 3,315 years and 6 months imprisonment.
- 31 journalists went to jail.
- 300 journalists were attacked.
- 3 journalists were shot dead.
- 300 days in which newspapers were not published.
- 13 major newspapers brought to trial
- 39 tonnes of newspapers and magazines destroyed
- 299 people lost their lives in prison.
The Council begins a program of forced assimilation of its Kurdish population.
The words “Kurds”, “Kurdistan” or “Kurdish” are officially banned.
The Kurdish language is prohibited in both public and private life.
People who speak, publish or sing in Kurdish are arrested and imprisoned.
(Even now in 2017, Kurds are still not allowed to get a primary education in their mother tongue and still don´t have a right to self-determination.

Above: Kurdish boys in Diyarbakir
Even now, there is ongoing discrimination against Kurds in Turkish society.)
The Council pushes the PKK to another stage…
PKK members have been executed, imprisoned and forced to flee to Syria (including Abdullah Ocalan).
10 November 1980, Strasbourg, France

Above: Strasbourg Cathedral
The Turkish Consulate is bombed causing significant material damage but no injuries.
In a telephone call to the office of Agence France Presse, a spokesman said the blast was a joint operation and marked the start of a “fruitful collaboration” between the ASALA (Armenian Secret Army for the Liberation of Armenia) and the PKK.
(Armenia has been officially independent since 1991.)
After the Council’s approval of the new Turkish Constitution in June 1982, General Evren organizes nationwide general elections, to be held on 6 November 1983.
This results in the one-party government of Turgut Ozal’s Motherland Party.

Above: Turgat Özal (1927 – 1993), 8th President of Turkey (1989 – 1993)
The Özal government empowers the police force with intelligence capabilites.
Beginning in 1984, the PKK initiates a guerilla offensive with a series of attacks on Turkish military and police targets.
Since 1984, 37,000 people have been killed.
The three coups of 1960, 1971 and 1980 revolutionized modern Turkey.
So, His Excellency Recep Erdogan´s instinct to (over)react to the 2016 attempted coup becomes somewhat understandable, for soldiers can overthrow governments.
(More about this later…)
Yesterday, Turkey´s Parliament in Ankara adopted a package of 18 amendments placing all executive powers in His Excellency’s hands.
His Excellency believes he has learned from these coups and his administration has revved up nationalist rheotric to justify a mounting crackdown against the Kurds, socialists and the press.
I believe His Excellency is mistaken.
Violence creates violence.
Rebellion incites suppression and suppression incites rebellion.
Revolution encourages revolution.
There is much that I see about Turkey that saddens me.
Like anyone not resident in Turkey I am limited to what I receive second-hand so I try to find as many sources of information as I can and hope through the complexity to find and share as unbiased and complete a picture as I can.
I am left with a few questions I will try and address in the third part of this essay on Turkey and the Kurds:
Is change possible without bloodshed?
How can change without bloodshed be realisable?
Surprisingly, hope will begin with the Özal government…
(To be continued…)

Sources: The Economist, 21 – 27 January 2017 / Wikipedia / Andrew Finkel, Turkey: What Everyone Needs to Know



